participant_demographics#
You can see the full contents of this project on GitHub.
participant_demographics#
Annotating information about participants: count, sex, age, and diagnosis.
Some analyses of this project’s annotations are shown in this page.
How to annotate#
Annotating demographic information about the participants is more complex than other projects in this repository, because studies typically involve several groups of participants, with diverse structures, and there is some variation in how the relevant information is reported. To annotate a piece of information about a group of participants, we stack several annotations on top of each other. We add annotations that identify the group of participants (eg patients vs controls), then an annotation that contains the information of interest (eg count, min age, etc.). To be easily linked these annotations should be at the exact same positions, which is easy to acheive in labelbuddy by clicking several labels in sequence (or by first selecting an existing annotation and then clicking a new label to add it on top).
We consider that most articles roughly conform to the participant group structure depicted in the tree shown in Fig. 1. The root contains all the participants, which are then divided in patients and healthy controls, each of which may contain several subgroups, and finally each subgroup can contain females and males. Note that for many articles, some of the nodes will be empty – eg studies involving only healthy controls, only one sex, etc.
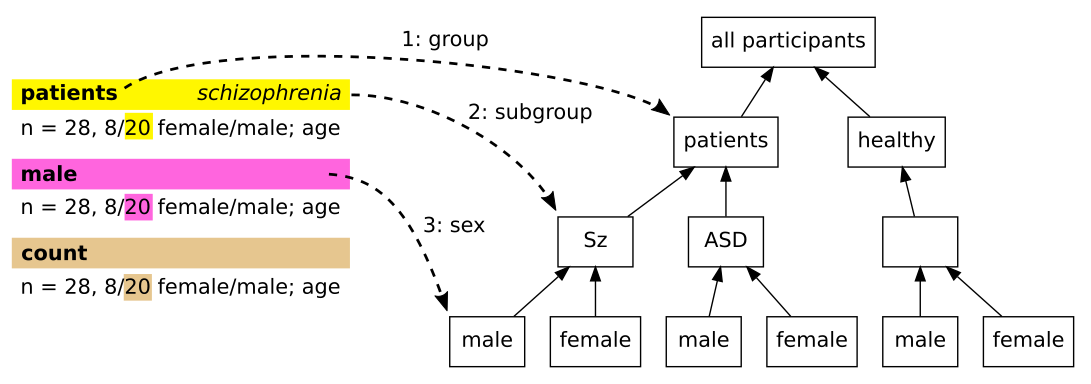
Fig. 1 The participant group structure and corresponding annotations.#
Annotation example with subgroups#
In Fig. 1 we see the general way of annotating information about participants. We start by describing the most complex case but for most annotations the situation will be simpler.
This video (without sound) illustrates the annotation process that is described below.
The report on the left shows a continuously updated summary of the participants in the current document, it is launched with the scripts/watch_participants.py script as explained here.
Here we annotate the count (20) of a specific subgroup, constituted of:
Patients
Within patients, the schizophrenia subgroup (this article also has an autism spectrum disorder subgroup of patients)
Within the schizophrenia subgroup, the males.
To annotate this information, we select the information we want to annotate and then apply labels, starting from the top of the participants tree (the actual order doesn’t matter, this is just a suggestion). We first click the “patients” label.
Then, as there are several patients subgroups in this article, we need to differentiate the schizophrenia subgroup. We don’t want to add new labels for subgroups, as we would end up with a very long list of labels, most of which are used in few papers (eg “schizophrenia”, “siblings”, “experts”, etc.) Instead, we rely on the extra data input field in labelbuddy. While the “patients” annotation is still selected, we write int its extra data field (on the bottom left of labelbuddy). We enter in there whatever name we want to give to the schizophrenia subgroup, which will act as a local identifier within the current paper. This name is arbitrary and only serves to link the different annotations about that subgroup, here we unoriginally chose “schizophrenia”. Referring it to it again for other annotations will be easy because labelbuddy will propose it in a completion list whenever we are entering extra data for the “patients” label.
Next, we click on the “males” label to create a new annotation, indicating that within the “patients” / “schizophrenia” subgroup, we are looking at the males. Finally, we click on the “count” label to create a new annotation, indicating the type of information contained in our selected text. If needed, we can use the extra data here again – for example if the count was indicated as “twenty” (in English), we would enter in the extra data “20” (the value in numbers), to make it easier to use the annotation later.
So to summarize, the steps are:
Select the group (“patients” or “healthy”)
Enter the subgroup identifier in the “extra data” field (with the help of the completion list if we have seen that subgroup before)
Select the sex (“females” or “males”)
Select the label that indicates the type of information (“count”, “age mean”, etc.)
If necessary add any complementary information in the “extra data” field (eg “20” when the selected text is “twenty”).
When we annotate information about nodes that are higher in the participant group tree, we simply omit the labels that do not apply. For example, if we are annotating the total count of participants (healthy and patients), we simply apply the label “count”, without indicating a group, subgroup or sex. As we see below, when we select the diagnosis, we only indicate the group and subgroup, as the diagnosis applies to both males and females.
Here are all the annotations for article discussed above, PMC8883821:
PMC8883821
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Disease-Specific Contribution of Pulvinar Dysfunction to Impaired Emotion Recognition in Schizophrenia
78 participants
Healthy participants
30 participants, 8 females, 22 males
Age range: 19 – 54 years
Patients autism spectrum disorder
Diagnosis: autism spectrum disorder
20 patients, 4 females, 16 males
Age range: 19 – 43 years
Patients schizophrenia
Diagnosis: schizophrenia
28 patients, 8 females, 20 males
Age range: 21 – 54 years
A simpler example#
When the participant structure of an article is simpler, we can omit any of the labels as long as it does not introduce an ambiguity.
For example, if there is only one group of patients, we do not need to indicate a subgroup.
If the study contains only patients or only healthy participants, we do not need to use the patients or healthy labels.
Which label applies will be inferred from the presence of a diagnosis.
The live report can help check that any information we leave out is being correctly inferred as we annotate.
Below is an example for the article PMC3447931 where only the count is provided, for the patients and for the healthy controls. Note that “diagnosis” implicitly refers to patients, so we can omit the group label here (but it would not be an error to add it).
PMC3447931
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Patterns of Spontaneous Brain Activity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Resting-State fMRI Study
40 participants
Healthy participants
20 participants
Patients
Diagnosis: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
20 patients
Participant demographics summaries#
The repository contains utilities to extract summaries about the participant groups from an article’s annotations and display them as shown in this page.
scripts/participants_report.py creates a report for all the articles exported from a given annotator and project.
scripts/watch_participants.py serves a live summary of the participant groups in the document we are currently annotating in labelbuddy.
From the root of the repository you can run it with:
scripts/watch_participants.py projects/participant_demographics/Your_Name.labelbuddy
(If you call it without specifying a file it will pick the most recently modified .labelbuddy file in the projects/ directory.)
It will print the path to a file that you can open in a web browser and that can help to check annotations are correctly interpreted as you create them. If possible, the report will be automatically opened in the default web browser.
See scripts/participants_report.py --help and scripts/watch_participants.py --help for details.
Some more examples#
Below are a few more examples of annotated documents to help annotators get started.
PMC2144768
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
What Are You Feeling? Using Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Assess the Modulation of Sensory and Affective Responses during Empathy for Pain
18 participants
Healthy participants
18 participants, 9 females, 9 males
Age range: 19 – 35 years
Age mean: 23.7 years
PMC2151069
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Dissociation of neural correlates of verbal and non-verbal visual working memory with different delays
12 participants
Healthy participants
12 participants, 6 females, 6 males
Age range: 20 – 40 years
Age mean: 25.4 years
PMC2390848
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Fast Visuomotor Processing of Redundant Targets: The Role of the Right Temporo-Parietal Junction
15 participants
Healthy participants
15 participants, 7 females, 8 males
PMC2494616
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Phantom limb pain, cortical reorganization and the therapeutic effect of mental imagery
13 participants
Patients
Diagnosis: phantom limb pain
13 patients, 2 females, 11 males
Age range: 32 – 75 years
Age mean: 52.9 years
PMC2525845
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
The functional anatomy of semantic retrieval is influenced by gender, menstrual cycle, and sex hormones
24 participants
Healthy participants
24 participants, 12 females, 12 males
PMC2561002
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Cortical Activations in Humans Grasp-Related Areas Depend on Hand Used and Handedness
34 participants
Healthy participants lh
15 participants, 10 females, 5 males
Age range: 21 – 35 years
Age mean: 26.1 years
Healthy participants rh
19 participants, 12 females, 7 males
Age range: 19 – 30 years
Age mean: 24.7 years
PMC2648877
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Atypical recruitment of medial prefrontal cortex in autism spectrum disorders: An fMRI study of two executive function tasks
33 participants
Healthy participants
18 participants, 5 females, 13 males
Age mean: 32.0 years
Patients
Diagnosis: Autism Spectrum Disorder
15 patients, 3 females, 12 males
Age mean: 38.0 years
PMC2748718
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
The Neural Correlates of Religious and Nonreligious Belief
30 participants
Healthy participants
30 participants, 16 females, 14 males
PMC2775905
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
On-line plasticity in spoken sentence comprehension: Adapting to time-compressed speech
18 participants
Healthy participants
18 participants
Age range: 18 – 60 years
Age mean: 26.7 years
Age median: 22.5 years
PMC2935390
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
The Brain Effects of Laser Acupuncture in Healthy Individuals: An fMRI Investigation
10 participants
Healthy participants
10 participants, 7 females, 3 males
Age range: 18 – 50 years
Age mean: 39.8 years
PMC2993660
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Imaging the functional connectivity of the Periaqueductal Gray during genuine and sham electroacupuncture treatment
48 participants
Healthy participants
48 participants, 24 females, 24 males
Age mean: 26.4 years
PMC2995581
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Face-Specific Resting Functional Connectivity between the Fusiform Gyrus and Posterior Superior Temporal Sulcus
30 participants
Healthy participants experiment 1
12 participants
Healthy participants experiment 2
18 participants
PMC3002948
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Affective Response to a Loved One's Pain: Insula Activity as a Function of Individual Differences
30 participants
Healthy participants eating disorders prone
15 participants, 5 females, 10 males
Age mean: 34.4 years
Healthy participants phobic prone
15 participants, 6 females, 9 males
Age mean: 39.2 years
PMC3045463
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Neurobehavioral Mechanisms of Temporal Processing Deficits in Parkinson's Disease
40 participants
Healthy participants
19 participants, 7 females, 12 males
Patients
Diagnosis: idiopathic Parkinson's Disease
21 patients, 7 females, 14 males
PMC3078751
See article on PMC
Labelled by Jerome_Dockes
in participant_demographics
Caudate Nucleus Signals for Breaches of Expectation in a Movement Observation Paradigm
14 participants
Healthy participants
14 participants, 8 females, 6 males
Age range: 22 – 29 years
Age mean: 24.8 years